以下內容翻譯自 linux input ecosystem (2010), by joe shaw
(還有我的幾張截圖 zzz)
目前 Linux kernel 的 input system 分成兩大塊,一個是 device driver ,另一個是 event driver 。
device driver 顯然地就是跟硬體溝通,
device driver 裡,大部分的 USB devices 都是由 usbhid driver 負責。
event driver 負責的則是把 device driver 產生的 events 丟到 userspace,
目前這邊主要是由 evdev 來完成,
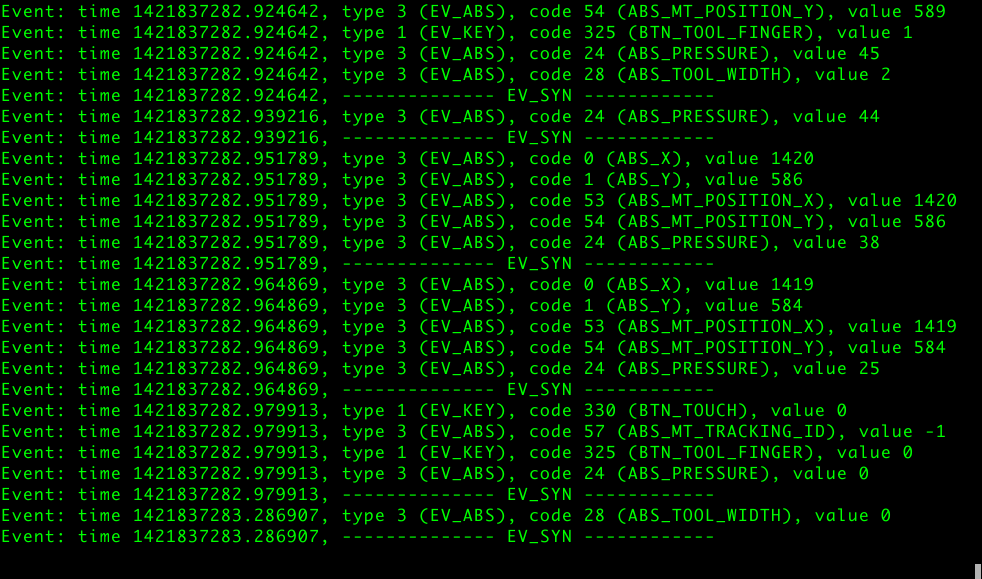
evdev 會建立 character devices (通常叫 /dev/input/eventN) 並且用 struct input_event 來溝通。
要取得 evdev 的 devices 和 events 的資訊可以使用 evtest
當一個 device 接上的時候,kernel 會為 device 在 sysfs 建立一個 entry,
並且產生 hotplug event,該 event 會由 udev 處理 (套一些 policy 和額外的 properties),
然後在 /dev 建立 device node,input devices 會套用 /lib/udev/rules.d/60-persistent-input.rules 裡的 rules,
其中還會 run /lib/udev/input_id tool 來從 sysfs node 取得 device 的 capabilities,
並且在 udev database 中設好環境變數 (例如: ID_INPUT_KEYBOARD, ID_INPUT_TOUCHPAD)。
除了前面提的東西外,
X 也有 udev config backend 會在 startup 以及 hotplug devices 進來時運作 (為不同 input devices 去 queries udev)。
X 會看不同的 ID_INPUT_* properties 來判斷目前是哪個 device (keyboad, mouse, touchpad, joystick, …),
這些資訊可以用於 xorg.conf.d 裡面的 InputClass sections
(例如: MatchIsPointer, MatchIsTouchpad, MatchIsJoystick, …)
# xorg.conf.d/50-synaptics.conf
Section "InputClass"
Identifier "touchpad catchall"
Driver "synaptics"
MatchIsTouchpad "on"
Option "TapButton1" "1"
Option "TapButton2" "2"
Option "TapButton3" "3"
Option "VertEdgeScroll" "1"
Option "VertTwoFingerScroll" "1"
Option "VertScrollDelta" "-58"
Option "HorizEdgeScroll" "1"
Option "HorizTwoFingerScroll" "1"
Option "HorizScrollDelta" "58"
Option "CircularScrolling" "1"
Option "CircScrollTrigger" "0"
Option "CircScrollDelta" "58"
Option "EmulateTwoFingerMinZ" "40"
Option "EmulateTwoFingerMinW" "8"
Option "CoastingSpeed" "0"
Option "FingerLow" "35"
Option "FingerHigh" "40"
EndSection
Xorg 在 input devices 的 driver (handler) 的地方可以是 evdev 、 synaptics 、 joystick 。
Linux 在 evdev 裡有一個良好的 generic event interface, 所以只需要少量 drivers 就能跟硬體互動 (因為他們不走 device-specific protocols)。 而 Linux 上的 drivers 當中,幾乎全部都是走 evdev 的介面,包含前面列的三個。
在 Linux 上, Xorg 的 evdev driver (generic input driver) 提供基本的 keyboard、 mouse、lid switches、power switches 等功能, 經由 evdev 的 interface 到 /dev/input/eventN devices。
至於 synaptics driver 呢,其實也是走 evdev 的 interface 來跟 kernel 溝通的。 在 Linux 上它不能跟硬體直接溝通,也不能弄 Synaptics™ hardware-specific。 synaptics driver 只是個從 evdev 分出去的 driver,加上了一些 touchpad 硬體要有的 features (例如: two-finger scrolling), 在 Linux 上它比較像是個 “touchpad” module,在其他 non-Linux 平台上則可以使用 Synaptics protocol。
而 joystick driver 的情況跟 synaptics driver 類似,走的也是 evdev 的 interface, 而不是 device-specific protocol。
X 的概念只包含了 keyboards 和 pointers,而 pointers 則包含了 mice、touchpads、joysticks、wacom tablets … etc。 X 另外還有 core keyboard 和 pointer 的概念,預設所有的 device 都是送 core events 到 applications 的, 但是可以把特定 devices 設為 non-core。
如果要收 non-core devices 的 events 的話,需要使用 XInput 或 XInput2 extensions。 XInput 提供 core-like 的 events (例如: DeviceMotionNotify、DeviceButtonPress), 所以跟 core events 用起來類似,但是 setup 方式和大部分的 X extensions 不一樣。